A Highlight of Thin Aluminium Sheet
Oct 31 25
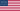
In numerous fields such as industrial manufacturing, architectural decoration, and electronics, thin aluminum sheets have become an indispensable material due to their advantages of being lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to process.

Thickness of thin aluminum sheets
Generally, the thickness of thin aluminum sheets typically ranges from 0.1mm to 6mm. Among these, the 0.1mm to 0.5 mm aluminium sheet is considered the ultra-thin aluminum sheet. They are commonly used in applications with strict weight and thickness limitations, such as precision gaskets inside electronic products and ultra-thin substrates for battery casings.
Thin aluminum sheets with a thickness of 0.5mm-2mm are the most widely used. They offer good ductility while maintaining sufficient strength. Common applications include aluminum ceiling panels in building decoration, advertising sign panels, and the outer casings of household appliances (such as microwave oven casings and air conditioner outdoor unit panels).
Thin aluminum sheets of 2mm-6mm are more suitable for applications requiring a certain level of strength, such as protective housings for small equipment, some interior parts in the automotive industry, and simple structural components. This thickness allows the aluminum sheet to maintain good dimensional stability under certain external forces.
Common alloys for thin aluminum sheets
1. 1000 aluminum alloys
1-series alloys have high purity, generally above 99.0%, with 1050, 1060, and 1100 being common grades. These thin aluminum sheets possess excellent thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, and corrosion resistance, and also have good processing performance, easily undergoing stamping, bending, and welding.
However, their strength is relatively low, making them unsuitable for applications requiring heavy loads. They are mainly used for decorative parts, heat sinks, conductive terminals, and food packaging containers.
2. 30000 series aluminum
3-series alloys use manganese as the main alloying element, with common grades including 3003 and 3004. The addition of manganese significantly improves the strength of the aluminum sheet compared to 1-series alloys, while maintaining good corrosion resistance and ductility, especially exhibiting excellent corrosion resistance in marine or humid environments.
In addition, 3-series alloy thin aluminum sheets also have good weldability, so they are often used to manufacture ship decorative panels, refrigerator liners, air conditioner evaporators, and pipe insulation shells.
3. 5000 aluminum alloys
5-series alloys use magnesium as the main alloying element, with common grades such as 5052, 5083, and 5754. The addition of magnesium gives these aluminum sheets high strength and high toughness, as well as excellent corrosion resistance, especially outstanding resistance to seawater corrosion. They are also relatively lightweight, belonging to lightweight materials.
However, 5-series alloy thin aluminum sheets are relatively difficult to process, especially prone to cracking during bending, requiring strict control of processing parameters. They are mainly used in structural components in the aerospace field, automotive body panels, bicycle frames, pressure vessels, and other applications requiring high strength and lightweight.
Cutting methods for thin aluminum sheets
Cutting thin aluminium sheet is a crucial step in the processing. Different thicknesses, materials, and application requirements necessitate the selection of appropriate cutting methods to ensure both quality and efficiency.
1. Manual Cutting: For thin aluminum sheets (generally below 0.5mm), small dimensions, and where high cutting precision is not required, manual cutting is suitable. Common tools include scissors and utility knives.
2. Mechanical Cutting: When the thickness of the aluminum sheet is between 0.5mm and 6mm, and batch cutting or a certain level of cutting precision is required, mechanical cutting is usually used. Common equipment includes shearing machines and punch presses.
3. Laser cutting: It is a high-precision and highly flexible cutting method suitable for thin aluminum sheets of various thicknesses, especially in scenarios requiring extremely high cutting accuracy (e.g., within 0.1mm) or complex irregular shapes. Laser cutting utilizes a high-energy-density laser beam to heat the thin aluminum sheet, causing it to rapidly melt, vaporize, or be blown away under the laser's action, thus achieving the cutting process.
https://www.alsheetplate.com/a/a-highlight-of-thin-aluminium-sheet.html